What Is the Blockchain
By now, most people have heard of Bitcoins. Bitcoins are one of the (now thousands) of cryptocurrencies available on the market. The original cryptocurrency has become hot property, with the total value of Bitcoins reaching $326.5 billion in December 2017.. What you might not realize, however, is that Bitcoins only exist because of a digital public ledger system called the Blockchain.
The Blockchain first appeared on the scene in November 2008. At that point, someone (or a group of people) going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a white paper called A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. The system described by Nakamoto was revolutionary. It created a way for a digital currency to exist, be shared, be bought and sold, and be used to buy and sell with. All this without the need for intermediary financial institutions.
Perhaps most importantly, thanks to the Blockchain’s peer-to-peer structure, the cryptocurrency that resided on the public ledger system would exist in a state that defied corruption. The Blockchain’s incorruptible backbone has since been noticed to have many more uses than just holding together cryptocurrencies.
Nowadays, more and more uses for the Blockchain are being developed, leading many people to ask what is the Blockchain and how does it work?
Understanding Blockchain: The Basics

The Blockchain is a public ledger system that keeps a record of all the Bitcoin transactions ever made. The public ledger system never sleeps. It is constantly being updated and shared between hundreds of thousands of computers attached via the web. Those computers are called nodes. Because there are so many of them being updated simultaneously, it is technically unfeasible to hack the entire system.
The data that makes up the Blockchain is referred to as a “chain.” It is the sum of all the transactions ever made, from the beginning of time until the very last transaction. The chain itself is formed by the network as it time-stamps the transactions that are made. Those time-stamps are made by hashing (encrypting) the transaction data into a hash-based “chain” of evidence of transactions.
In Nakamoto’s original white paper about the Blockchain, this chain of data is referred to as "a system for electronic transactions without relying on trust."
With Blockchain technology, there is no single person, entity, or institution, that anyone has to put their faith in. The chain provides a flawless record of all the transactions that have ever been made. This is commonly referred to as ‘proof of work.’ That proof of work cannot be altered without going back and redoing it. However, because it has already happened and been hashed into the chain, the work can’t be redone.
How Blockchain Currency Avoids Double Spending
The problem with digital data is that it is easily copied and reproduced. Thus, for a long time, having a digital currency was considered impossible. How could digital coins be made unique, so that they could only be spent once? Nakamoto’s Blockchain was the solution to this conundrum.
By decentralizing the ledger of transactions, the entire network of nodes attached to the Blockchain is able to constantly stay aware of the location of every Bitcoin in the system. This solves the problem of double spending, allowing cryptocurrencies to flourish.
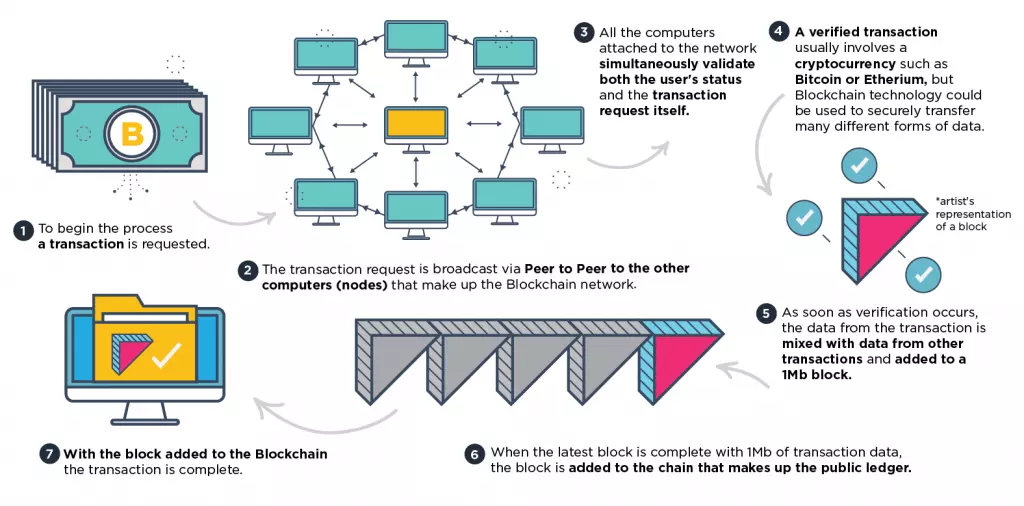
How Does Blockchain Work in Practice?
- Firstly, someone asks to perform a transaction using the Blockchain. At this point, a request is sent via the internet to all nodes currently attached to the Blockchain. The nodes (participating computers) each receive the request and the transaction process begins.
- Next, the network of nodes simultaneously validates both the user’s status within the Blockchain and the transaction request. This is performed using recognized algorithms. With the person who requested the transaction validated, and all nodes in agreement about the request, the transaction can move forward.
- A verified transaction can involve moving cryptocurrency from one place to another in order to purchase something or to store it in a different location. However, Blockchain technology can also be applied to verify any other data that needs to be securely transacted. That includes data records, contracts, and other data or information that needs to be shared in a trustful manner.
- With the transaction verified, it can be moved into the completion stage of the process. This is achieved by adding the data from that particular transaction to data from other transactions into what is called a block. The blocks are each 1 Mb in size and they are created approximately once every ten minutes. They hold all of the most recent transactions made in the block chain.
- Now that the data has been added to a block - and the block is complete with 1 Mb of data transactions - the block is added to the chain of blocks. Thus the original transaction is complete (as are all the other recent transactions making up that block).
Blockchain Security: The Sum of All Transactions
It is that completed chain of blocks that makes up the incorruptible public ledger of transactions known as the Blockchain. The longest chain on the network serves as proof of the entire history of transactions. It is shared with nodes as they join the network.
The beauty is that there is no centralized database of transactions for a cybercriminal to hack. Instead, the Blockchain exists as a public database. It is continually shared and reconciled between all of the nodes attached to the network. As the network is made up of millions of host computers, the Blockchain is immensely secure.
This makes the data contained within the Blockchain easily verifiable. In the case of Bitcoin, this gives an already finite currency a massive benefit (and therefore innate value) by making it invulnerable to corruption at the hands of financial institutions or other outside forces.
As time passes, the chain of 1 Mb blocks gets bigger and bigger. For people who haven’t updated their version of the (Bitcoin) Blockchain in a while - or are downloading it for the very first time to a new Bitcoin Blockchain wallet - acquiring it can thus take quite a long time (anything from a few hours to weeks).
As the Blockchain gets bigger and bigger, this time will inevitably increase. For this reason, there is sometimes talk of "hard fork" scenarios. This would see all Bitcoin Blockchain users forced to move (hard fork) into a new version of the Blockchain.

Bitcoin & Blockchain explained: The Hard Fork Debate
The debate about a Bitcoin hard fork has been raging for some time. Many Bitcoin experts believe that the 1 Mb blocks are going to become too limiting. The concern is that, as the chain of blocks becomes longer, the complex cryptographic process needed to verify the chain will become laggy and slow.
Everyone understands the frustration of lagging (or buffering) from watching streaming video. Now imagine that effect impacting a global currency. Financial experts understand that any lagging within the Blockchain - which affects Bitcoin's liquidity - could have a negative effect on the value of Bitcoins. This, naturally, is a massive concern to investors.
There is general agreement that a hard fork is necessary to curb the lagginess problem. However, nobody knows how a hard fork might affect the price of Bitcoin. The Blockchain is the backbone that holds the popular cryptocurrency together. The trust that surrounds Bitcoins is primarily leveraged on that technology working behind the scenes. As such, an investment in Bitcoin is actually an investment in the Blockchain.
For this reason, there is enormous concern among investors that a new Blockchain could fail. This could cause Bitcoin to suffer a catastrophic loss in value.
Which Hard Fork is Best?
One would imagine that the possibility of the Blockchain becoming laggy was more troubling than a hard fork, especially when the Blockchain of a rival cryptocurrency (Ethereum) has already proven that a hard fork can be managed successfully (twice actually: once by accident).
Another problem for the Bitcoin Blockchain, however, is that nobody can agree on what form the hard fork should take. There are two rival options: Bitcoin Unlimited (BU) and Segregated Witnesses (SegWit). BU would hand more power to Bitcoin miners. It would allow the Blockchain to upscale again and again whenever it was necessary. SegWit retains a decentralized approach, but only doubles the bandwidth of the Blockchain. That means that one day another hard fork would likely need to be implemented.
For now, nobody is sure what is going to happen. When the hard fork does happen, Bitcoin will essentially become a different currency on the new Blockchain (with the original Bitcoin on the original Blockchain). If everybody migrates willingly into the new fork then everything should be fine. However, unless everybody accepts the new Blockchain (and in the case of the Ether hard fork not everyone did), it is possible that mutiny could negatively affect the price of the cryptocurrency.

Blockchain Technology: What else can it be used for?
Traditional database hold one central copy of information, which can only be updated by one actor at a time. The Blockchain, on the other hand, permits a dataset to be changed by multiple parties simultaneously. When a bank transfers money, for example, it must first lock access to the funds while it makes the transfer. Following that, it must update the other side, and then re-open access to the funds.
Blockchain banking allows money transfers to happen more quickly and efficiently. Thus financial institutions like Barclays, BNP Paribas, Nasdaq, and even the Federal Reserve, have been investing time and money in projects that investigate the use of Blockchain technology for their own purposes.

It is not just for financial transactions, however, that Blockchain technology offers value. A firm called Gyft is using blockchain technology to offer gift cards to small and midsize businesses. For many businesses, the cost of providing gift cards is too great to implement. With Gyft, however, any firm can easily roll out gift cards that are redeemable at any of their stores.
Factom is another of those innovations. It is an extension of the initial Blockchain protocol that allows a blockchain to be used to handle larger data sets. Factom allows users to run their own personal secure ledgers. Those users are able to define what information is stored within their ledger. This allows the Factom blockchain to address data handling in other business areas, such as law.
Blockchain Banking: Just the Beginning
The value of Blockchain technology is already manifesting all around us. It's seen not only in the price of Bitcoins, but in other cryptocurrencies that run on similar public ledgers. The most exciting of these are currently Ethereum, Litecoin, and ZCash. These cryptocurrencies have all seen an explosion in their value over the last year, and things seem set to continue in the same direction.

What’s more, this is a relatively new technology. That means its true value is still being discovered. There may be further advances in the way it is implemented as time goes on.
For now, Bitcoin is ahead of the pack, but it would only take a few advances in blockchain technology for another coin (with perceived greater value due to its improved blockchain) to enter the market. With this in mind, anybody interested in investing in cryptocurrencies should really be watching emerging blockchains for innovations if they want to spot tomorrow's big winner.
In addition, there are people all over the world working hard to find novel ways to incorporate blockchain technology into other businesses. To my mind, because blockchain tech is so advantageous, some of those applications are set to succeed, and in all likelihood will become hugely successful businesses of the future.
Cryptocurrencies and VPN services
Finally, anybody that is interested in Blockchain and cryptocurrencies is strongly advised to look into VPN services. VPNs allow people to protect their passwords and logins with encryption, adding an extra layer of security to all their online transactions.
Title image credit: pichetw/Shutterstock.com
Image credits: Zapp2Photo/Shutterstock.com, varuna/shutterstock.com, 3Dsculptor/Shutterstock.com, Roman Pyshchyk/Shutterstock.com
